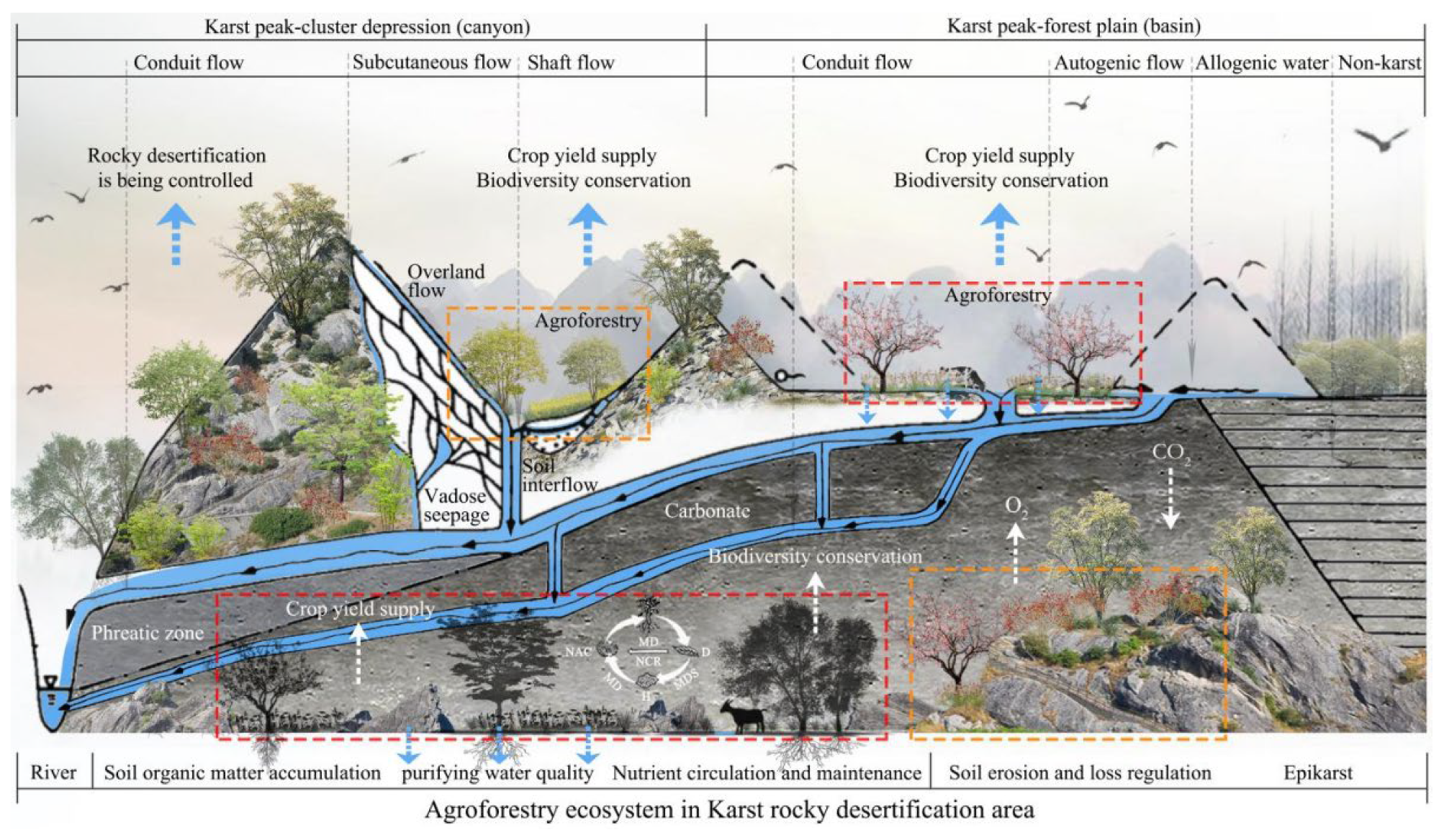
Bird Diversity in Agroforestry: Eco-Balance in the Tropics
Bird diversity in agroforestry enhances ecosystem health and sustainability. It offers significant benefits for tropical landscapes.
Agroforestry integrates trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes. This practice supports diverse bird species, which contribute to pest control, pollination, and seed dispersal. Birds in agroforestry systems help maintain ecological balance and boost crop yields. These benefits are vital for tropical regions facing deforestation and biodiversity loss.
Agroforestry also provides habitats for endangered bird species, promoting conservation. Farmers adopting agroforestry practices can achieve sustainable farming and biodiversity conservation. This approach creates resilient ecosystems and supports rural livelihoods. Embracing bird diversity in agroforestry is a step toward a sustainable future for tropical landscapes.
Introduction To Bird Diversity In Agroforestry
Bird diversity in agroforestry plays a crucial role in tropical landscapes. Birds contribute to the balance and health of these ecosystems. Understanding their role helps create sustainable agricultural practices.
Importance Of Birds In Ecosystems
Birds are essential for seed dispersal and pest control. They help pollinate plants and maintain biodiversity. Birds also serve as indicators of environmental health.
| Bird Function | Impact on Ecosystem |
|---|---|
| Seed Dispersal | Promotes plant diversity |
| Pest Control | Reduces crop damage |
| Pollination | Increases plant reproduction |
| Environmental Indicators | Reflects ecosystem health |
Agroforestry Basics
Agroforestry combines agriculture and forestry practices. It integrates trees and shrubs into farming systems. This method enhances biodiversity and sustainability.
- Silvopasture: Combines trees with livestock grazing.
- Alley Cropping: Rows of trees with crops in between.
- Forest Farming: Cultivates crops under a forest canopy.

Credit: www.mdpi.com
Tropical Agroforestry And Habitat Diversity
Bird diversity plays a critical role in tropical agroforestry systems. These systems offer rich habitats that support various bird species. The integration of trees with crops creates a complex ecosystem. This complexity fosters greater biodiversity and sustainability.
Characteristics Of Tropical Agroforestry
Tropical agroforestry blends agricultural crops with forest trees. This practice creates diverse landscapes. These landscapes include fruit trees, timber trees, and shade trees. Each tree type offers unique benefits to the ecosystem.
Fruit trees provide food for birds and humans. Timber trees offer nesting sites for various bird species. Shade trees help regulate temperature and humidity. Together, these trees create a balanced and sustainable environment.
Habitat Structures And Bird Species
The habitat structures in tropical agroforestry are varied. These structures include tree canopies, underbrush, and open fields. Each structure supports different bird species.
| Habitat Structure | Supported Bird Species |
|---|---|
| Tree Canopies | Parrots, Toucans |
| Underbrush | Quails, Thrushes |
| Open Fields | Sparrows, Finches |
Tree canopies offer shelter and food for parrots and toucans. Underbrush provides cover for quails and thrushes. Open fields are ideal for sparrows and finches.
These diverse habitats create a rich environment. This environment supports various bird species, enhancing biodiversity.
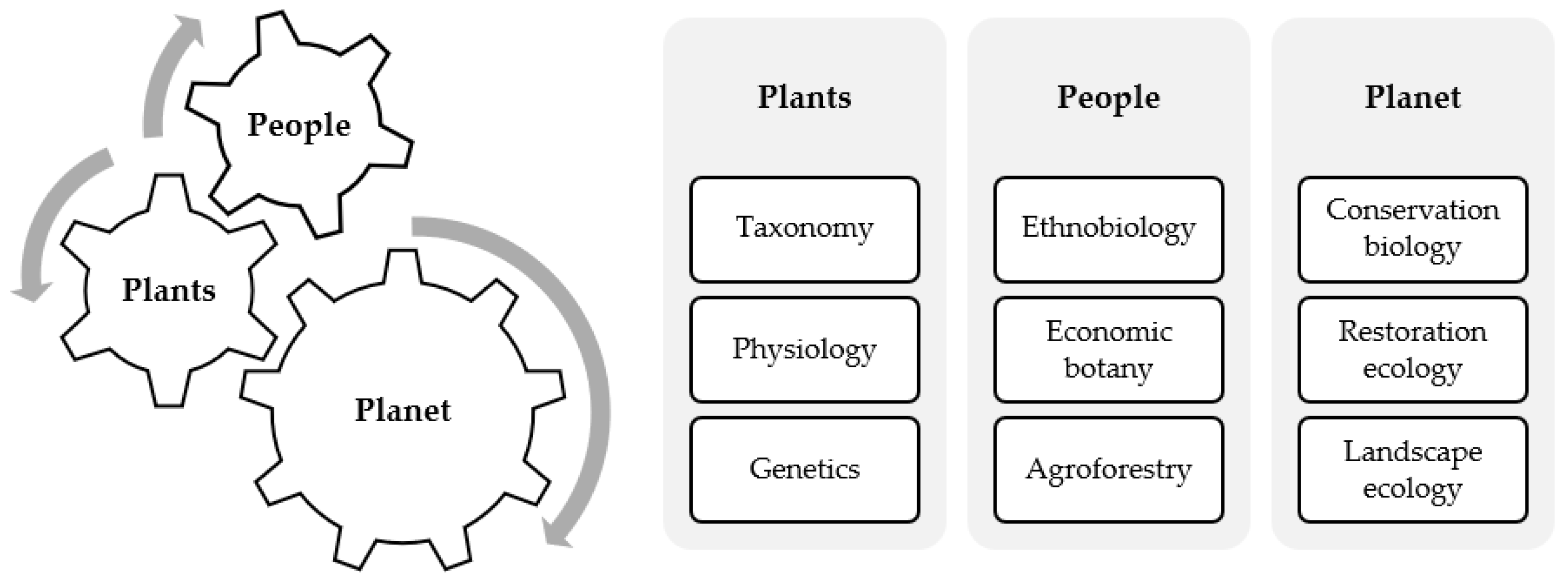
Bird Species Unique To Agroforestry Systems
Agroforestry systems blend agriculture and forestry. This creates diverse habitats for birds. These systems support unique bird species. Birds thrive here due to the mix of trees and crops. Let’s explore endemic birds and migratory patterns.
Endemic Birds Of Tropical Regions
Many tropical regions have unique birds. Agroforestry systems help these birds survive. Some birds are only found in these areas. These birds are called endemic birds. They depend on the diverse habitats agroforestry provides.
| Bird Species | Region | Habitat Preference |
|---|---|---|
| Golden-headed Quetzal | Central America | Shaded coffee plantations |
| Rufous-tailed Jacamar | Amazon Basin | Agroforestry plots |
| Buff-throated Saltator | South America | Mixed-crop farms |
Migratory Patterns Affected By Agroforestry
Migratory birds travel long distances. Agroforestry impacts their routes. These systems offer rest and food. Birds stop here during their journeys.
Some birds change their migratory patterns. They find better habitats in agroforestry areas. This helps birds stay healthy and strong.
- Food sources: Diverse plants attract insects, fruits, and seeds.
- Shelter: Trees provide safe resting spots.
- Climate regulation: Trees help keep the temperature stable.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Benefits Of Bird Diversity In Agroforestry
Bird diversity plays a vital role in agroforestry systems. Birds help create a balanced ecosystem. They provide numerous ecological services. These services are essential for sustainable tropical landscapes.
Pest Control By Avian Species
Birds act as natural pest controllers. They feed on insects and pests. This reduces the need for chemical pesticides.
- Birds eat insects that harm crops.
- They keep pest populations under control.
- This helps maintain healthy crops.
Using birds for pest control is eco-friendly. It promotes a healthier environment. It also boosts crop productivity.
Pollination And Seed Dispersal
Birds play a key role in pollination. They help plants reproduce. Birds also assist in seed dispersal.
- Birds carry pollen from flower to flower.
- This helps plants produce fruits and seeds.
- Birds eat fruits and spread seeds.
- They help plants grow in new areas.
Pollination by birds increases plant diversity. Seed dispersal helps in forest regeneration. Both actions support a thriving ecosystem.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Natural Pest Control | Birds reduce the need for chemical pesticides. |
| Pollination | Birds help plants reproduce by carrying pollen. |
| Seed Dispersal | Birds spread seeds, aiding forest regeneration. |
Embracing bird diversity in agroforestry promotes sustainable practices. It supports healthier ecosystems and enhances agricultural productivity.
Threats To Birds In Tropical Agroforestry
Birds face many challenges in tropical agroforestry systems. These threats impact their survival and diversity. Understanding these challenges helps us protect them better.
Habitat Loss And Fragmentation
Habitat loss is a major threat to birds in tropical agroforestry. Forests are cleared for agriculture, reducing available habitats. This leads to fewer nesting and feeding sites.
Fragmentation splits large habitats into smaller patches. Birds need large, continuous areas to thrive. Smaller patches lead to isolated populations. These populations face higher risks of extinction.
| Threat | Impact on Birds |
|---|---|
| Habitat Loss | Fewer nesting and feeding sites |
| Fragmentation | Isolated populations, higher extinction risk |
Pesticide Use And Its Impact
Pesticides are used to control pests in agroforestry. These chemicals harm birds directly and indirectly.
- Direct poisoning occurs when birds ingest chemicals.
- Indirect effects happen when their food sources are contaminated.
Pesticide impact reduces bird populations. Contaminated insects and plants harm birds. Long-term exposure leads to reproductive failure and death.
Conservation Efforts For Avian Populations
Bird diversity in agroforestry is vital for tropical landscapes. Conservation efforts help protect these avian populations. This section explores protected areas, buffer zones, and community engagement.
Protected Areas And Buffer Zones
Protected areas serve as safe havens for birds. They ensure birds have a habitat free from harm. Buffer zones act as barriers to human activities. These zones reduce the impact on bird habitats.
Creating these zones involves careful planning. Authorities map out crucial bird areas. They then set boundaries and enforce rules. This approach helps maintain the natural balance.
Benefits of Protected Areas:
- Maintains bird habitats
- Reduces human interference
- Supports bird breeding and feeding
Examples of Buffer Zones:
| Region | Type of Buffer Zone |
|---|---|
| Amazon Rainforest | Forest buffer zones |
| Southeast Asia | Agroforestry buffer zones |
Community Engagement And Education
Local communities play a key role in bird conservation. Engaging them helps protect avian populations. Education programs raise awareness about the importance of birds.
Workshops and training sessions teach sustainable practices. Community members learn how to coexist with birds. This knowledge empowers them to take action.
Effective Community Engagement Strategies:
- Conduct regular workshops
- Develop educational materials
- Promote sustainable farming techniques
Community engagement leads to lasting change. It fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility. Educated communities are more likely to protect bird habitats.
Sustainable Agroforestry Practices
Sustainable agroforestry practices blend agriculture with tree cultivation. This method enhances biodiversity and soil health. Birds thrive in these diverse landscapes, contributing to ecosystem balance. Let’s explore how organic farming and thoughtful agroforestry design support bird diversity.
Organic Farming And Biodiversity
Organic farming avoids synthetic chemicals, creating safer habitats for birds. Birds find ample food sources in organic farms. These farms support a variety of plants and insects. Birds help control pests naturally, reducing the need for pesticides. This creates a healthier environment for all living beings.
- Natural pest control
- Rich food sources
- Safe nesting areas
Agroforestry Design And Management
Effective agroforestry design includes trees, crops, and livestock. This mix creates diverse habitats for birds. Trees provide shelter and nesting sites. Crops and livestock offer additional food sources. Proper management ensures these elements work together harmoniously.
Using native tree species supports local bird populations. Diverse plant species attract different bird species. This diversity strengthens the ecosystem. Proper spacing and layering of plants improve habitat quality.
| Element | Benefit to Birds |
|---|---|
| Native Trees | Provide shelter and nesting sites |
| Diverse Plants | Attract various bird species |
| Crops | Offer food sources |
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Case Studies: Success Stories In The Tropics
Agroforestry systems have shown promise in conserving bird diversity in tropical landscapes. Here, we explore some remarkable case studies that highlight the success stories of bird population recovery and long-term eco-balance in these regions.
Recovery Of Bird Populations
In Costa Rica, a coffee plantation transformed into an agroforestry system. Native trees were planted among coffee plants. This led to a significant increase in bird species.
- Before transformation: 30 bird species
- After transformation: 60 bird species
This change provided nesting sites and food sources for birds. Many species returned, including the Resplendent Quetzal and the Keel-billed Toucan.
Long-term Benefits Of Eco-balance
A study in Kenya showed the long-term benefits of agroforestry. Farmers integrated fruit trees and crops on their lands.
| Year | Number of Bird Species |
|---|---|
| 2000 | 20 |
| 2010 | 45 |
| 2020 | 70 |
The increase in bird species created a balanced ecosystem. Birds helped control pests and pollinate plants. This reduced the need for chemical pesticides.
In the Philippines, a reforestation project combined agroforestry with conservation. Farmers planted native trees alongside crops. This created habitats for endangered bird species.
- Increased biodiversity
- Improved soil health
- Enhanced water quality
These benefits ensured a sustainable future for tropical landscapes. The success stories show the potential of agroforestry in promoting biodiversity.
Future Directions In Agroforestry
Agroforestry plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable agriculture while preserving biodiversity. The integration of trees, crops, and livestock creates a balanced ecosystem. This supports a variety of bird species. Understanding future directions in agroforestry is essential. It helps shape a sustainable future for tropical landscapes.
Research And Monitoring Of Bird Diversity
Ongoing research is vital for understanding bird diversity in agroforestry systems. Scientists use various methods to monitor bird populations. These include bird counts, acoustic monitoring, and satellite tracking. Data collection helps identify trends and patterns in bird diversity.
Research findings guide the development of better agroforestry practices. They ensure habitats support diverse bird species. Studies focus on the relationship between tree species, crop types, and bird populations. This information helps farmers create bird-friendly environments.
Here are some key research areas:
- Bird Surveys: Regular bird counts in different agroforestry systems.
- Acoustic Monitoring: Using technology to record bird calls.
- Satellite Tracking: Monitoring bird migration patterns.
Policy Implications And Global Impact
Effective policies are essential for promoting agroforestry. They support bird diversity and sustainability. Policymakers need to recognize the benefits of agroforestry. They should create incentives for farmers to adopt these practices.
International cooperation is crucial for the success of agroforestry. Countries must work together to promote sustainable practices. Sharing knowledge and resources can lead to better outcomes for bird diversity.
Global initiatives can support agroforestry development. These include funding research and providing technical assistance. Policymakers should focus on:
- Incentives: Financial support for farmers practicing agroforestry.
- Education: Training programs on sustainable practices.
- Collaboration: Partnerships between countries and organizations.
Agroforestry policies can have a significant impact on global bird diversity. Proper implementation ensures a sustainable future for tropical landscapes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Are Green Spaces Important For Bird Diversity?
Green spaces provide essential habitats for birds. They offer food, shelter, and nesting sites. Diverse plant life supports various bird species. Urban green spaces help maintain bird populations and biodiversity.
Why Is Biodiversity Of Birds Important?
Bird biodiversity ensures ecosystem balance, pest control, and pollination. Birds contribute to seed dispersal and genetic diversity. Their presence indicates healthy environments.
What Is Bird Diversity In Agroforestry?
Bird diversity in agroforestry refers to the variety of bird species found in agricultural landscapes that integrate trees. These birds play crucial roles in pest control, pollination, and seed dispersal.
How Does Agroforestry Benefit Bird Species?
Agroforestry provides diverse habitats and food sources for birds. It supports various species by offering nesting sites and protection from predators.
Conclusion
Bird diversity in agroforestry is crucial for sustainable tropical landscapes. It promotes ecological balance and enhances biodiversity. Embracing agroforestry practices can lead to a healthier environment. This benefits both wildlife and human communities. By supporting such initiatives, we contribute to a more sustainable future for our planet.


